In latest preclinical fashions, the inhalation of a mix of dwelling Lactobacilli micro organism attenuated pulmonary irritation and improved lung operate and construction for the power lung ailments bronchopulmonary dysplasia and power obstructive pulmonary illness.
This research, revealed within the journal Nature Communications, decided the mechanism of this reside biotherapeutic product—a powder combination of dwelling Lactobacilli micro organism—to scale back neutrophilic irritation and cut back a broad swath of inflammatory markers in BPD and COPD, says Charitharth Vivek Lal, M.D., a University of Alabama at Birmingham neonatologist who co-led the analysis with Amit Gaggar, M.D., Ph.D., a UAB pulmonologist.
Their findings “present a paradigm for the development of structural lung illness,” Lal stated, as a result of it identifies the Lactobacilli as essential to regulating lung protease exercise that’s linked to the destruction brought on by matrikine era, extracellular matrix turnover and power neutrophilic irritation that damages air sacs within the lungs.
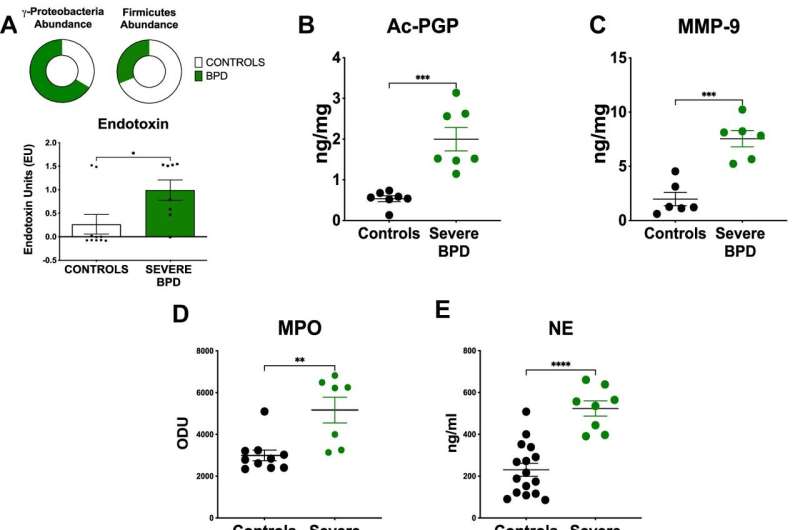
A attainable protecting position for Lactobacilli within the lung and the attainable use of Lactobacilli to deal with power lung illness had its basis in 2016 when Lal and UAB colleagues found that the airways of infants with extreme bronchopulmonary dysplasia had decreased numbers of Lactobacilli, elevated numbers of proteobacteria and elevated concentrations of proteobacterial endotoxin.
In this newest research, the UAB researchers present a mechanism of motion for the Lactobacilli remedy to lower downstream illness improvement and confirmed security and effectiveness of the reside biotherapeutic remedy in a mouse pup mannequin for BPD and three mouse fashions of COPD.
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia develops in some extraordinarily untimely infants after injury induced by excessive oxygen rigidity or mechanical air flow wanted to maintain them alive. COPD happens in older individuals, particularly people who smoke, and kills about 130,000 Americans a yr and about 3 million extra worldwide.
“Inhaled reside biotherapeutic merchandise present promise in addressing frequent pathways of illness development that sooner or later might be focused at quite a lot of lung ailments,” Lal stated. “Preclinical animal information is suggestive, and security of the potential drug in people shall be examined in a forthcoming medical trial. Human grownup security information in COPD will assist de-risk the pathway to approval to be used of the drug in bronchopulmonary illness infants.”
The UAB researchers hypothesized that mouse fashions of BPD would present heightened ranges of acetylated proline-glycine-proline, or Ac-PGP, an extracellular matrix-derived peptide, as had been seen in untimely infants with BPD.
This was demonstrated in BPD mouse fashions, and gain- or loss-of-function research confirmed the impression of Ac-PGP. Intranasal instillation of Ac-PGP elevated neutrophilic irritation and lung degradation. When an inhibitor of Ac-PGP was given with the Ac-PGP, markers of neutrophilic irritation decreased and lung construction improved.
Researchers then confirmed {that a} proprietary Lactobacilli mix of L. planatarum, L. acidophilus and L. rhamnosus carried out finest in synergy to scale back the inflammatory proteinase MMP-9, which helps launch the Ac-PGP from extracellular matrix. Furthermore, supernatant from Lactobacilli progress medium additionally diminished MMP-9 at the same magnitude as reside Lactobacilli micro organism.
A key discovering was that L(+) lactic acid, which is produced in Lactobacilli progress medium supernatant, diminished MMP-9 in vitro, displaying an essential position for this lactic acid as an anti-inflammatory molecule. Researchers discovered that reside Lactobacilli within the lungs supplied an ongoing, sustained launch of L(+) lactic acid in a managed and well-tolerated method.
A significant technological advance reported within the research was creating the inhaled Lactobacilli powder by way of particle engineering—particles sufficiently small to succeed in deep into the lungs whereas preserving viable micro organism. This reside biotherapeutic product was then examined within the BPD and COPD fashions. In the COPD mouse fashions, the mix efficiently diminished irritation within the lung microenvironment—whether or not handled concurrently or post-injury—displaying anti-inflammatory results, lower of a number of pro-inflammatory markers and elevation of the anti-inflammatory marker IgA.
An attention-grabbing discovering was the favorable efficiency of the reside biotherapeutic product. It diminished MMP-9 and different pro-inflammatory cytokines in addition to—or in some instances higher than—fluticasone furoate, a United States Food and Drug Administration-approved inhaled corticosteroid present in COPD mixture therapies.
Safety and biodistribution research in one of many COPD mouse fashions confirmed that inhalation of the bacterial powder didn’t provoke hostile reactions or illness, and the Lactobacilli didn’t translocate to distal tissues or accumulate within the lungs.
Co-first authors of the research are Teodora Nicola and Nancy Wenger, UAB Department of Pediatrics, Division of Neonatology. Other authors, together with Lal, Gaggar, Nicola and Wenger, are Xin Xu, Camilla Margaroli, Kristopher Genschmer, J. Edwin Blalock, UAB Department of Medicine, Division of Pulmonary, Allergy and Critical Care Medicine; and Michael Evans, Luhua Qiao, Gabriel Rezonzew, Youfeng Yang, Tamas Jilling, Kent Willis and Namasivayam Ambalavanan, UAB Department of Pediatrics, Division of Neonatology.
More info:
Teodora Nicola et al, A Lactobacilli-based inhaled reside biotherapeutic product attenuates pulmonary neutrophilic irritation, Nature Communications (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-51169-0
University of Alabama at Birmingham
Citation:
Inhalation of reside Lactobacilli lessens lung irritation and improves lung operate, preclinical research finds (2024, August 21)
retrieved 22 August 2024
from
This doc is topic to copyright. Apart from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.

