A brand new paper printed within the journal Nature Communications explores programmed cell demise (PD-1) in melanoma cells and the immune system’s response.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors are most cancers preventing medication that assist the immune system do its job of detecting and attacking tumor cells. Programmed cell demise 1 (PD-1) is a standard goal for the sort of drug—it’s a protein that sits on the floor of T cells and helps regulate the immune system’s response to neighboring cells, each regular and cancerous. While most analysis efforts to this point have centered on PD-1’s function in T cells, it’s also energetic in lots of different kinds of cells—together with most cancers cells, as first demonstrated by the Schatton laboratory at Brigham and Women’s Hospital.
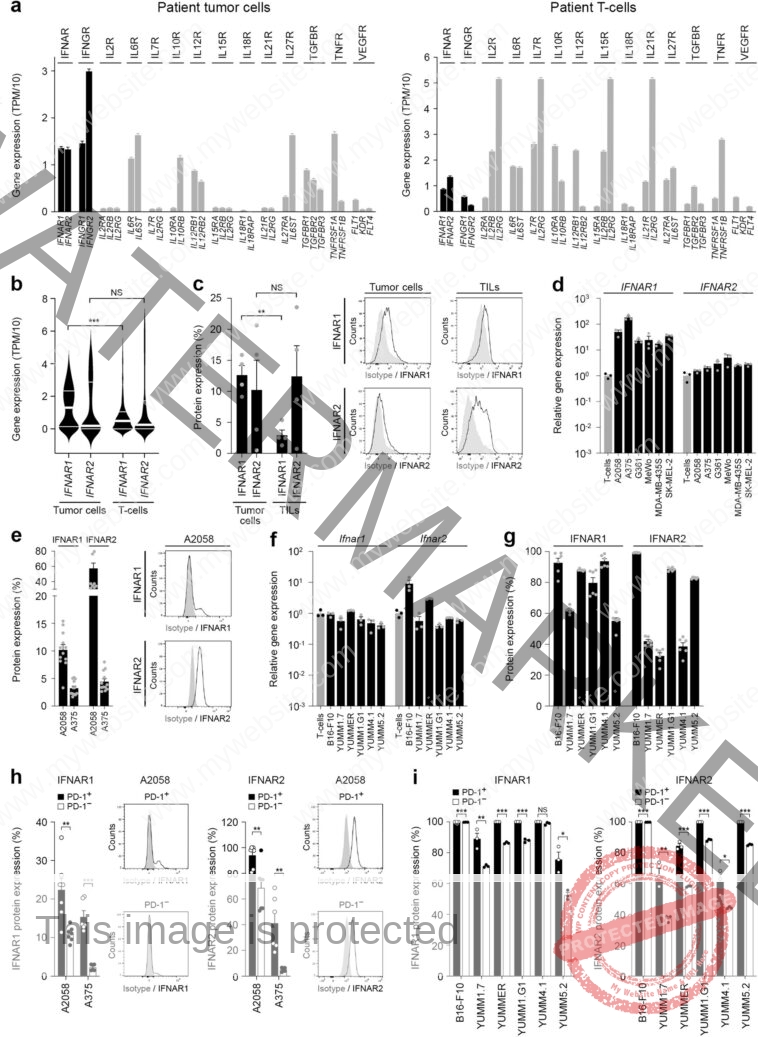
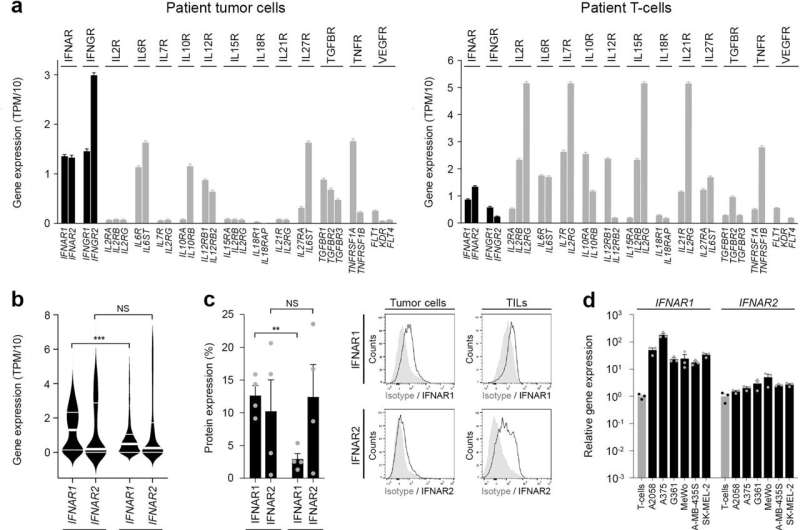
The researchers aimed to outline the molecular mechanisms controlling PD-1 expression and its therapeutic focusing on in melanoma cells. The group recognized a melanoma cell-intrinsic kind I interferon-JAK/STAT signaling circuit regulating the quantity of PD-1 in tumor cells.
They additional found that inhibition of this pathway not solely reversed induction of PD-1 in melanoma cells, but additionally lowered the efficacy of PD-1 checkpoint remedy. The work thus cautions towards combining JAK or IFNAR antagonists with PD-1 inhibitors, provided that this routine might weaken the effectiveness of immune checkpoint monotherapy.
This work builds off beforehand printed research figuring out PD-1 as a tumor cell-intrinsic development selling receptor in melanoma and Merkel cell carcinoma, the inhibition of which suppresses most cancers development. Here, researchers newly outline a regulatory pathway controlling PD-1 ranges in melanoma cells and the way inhibition of this pathway unintentionally disrupts therapeutic efficacy of immune checkpoint blockade. These findings may very well be used to optimize immunotherapeutic responses for sufferers with melanoma, and doubtlessly even different most cancers varieties.
To perceive the mechanisms that govern PD-1 checkpoint expression in melanoma cells, the researchers centered on established cytokine networks identified to control PD-1 in immune cells. They hypothesized that these mediators would have an identical function in modulating melanoma cell-PD-1 ranges.
Through their work, they found {that a} kind I interferon cytokine pathway intrinsic to melanoma cells critically controls tumor cell-PD-1 expression. They additionally discovered that disruption of kind I interferon signaling reduces melanoma-PD-1 expression and resultant efficacy of immune checkpoint remedy.
Type I interferon antagonists, together with JAK inhibitors and IFNAR1 antibodies, at present prescribed within the clinic for a number of autoimmune circumstances resembling psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, vitiligo and lupus might doubtlessly suppress the efficacy of PD-1 immune checkpoint remedy. The work thus raises concern over utilizing PD-1 checkpoint antibodies (e.g. nivolumab or pembrolizumab) with JAK inhibitors (e.g. ruxolitinib, utabacitinib, deucravacitinib) or IFNAR1 antibodies (e.g. anifrolumab).
Next steps embrace dissecting roles of kind I interferon signaling and inhibition not solely in melanoma cell-PD-1 expression, focusing on, and checkpoint efficacy, but additionally in extra most cancers varieties in addition to in various immune and non-immune cell lineages inside the tumor microenvironment.
Identifying extra regulatory networks controlling tumor cell-PD-1 expression and their results on immunotherapeutic outcomes are additionally main thrusts of ongoing analysis. The total aim is to leverage these findings to enhance immune checkpoint therapeutic responses in most cancers sufferers.
More data:
Julia Holzgruber et al, Type I interferon signaling induces melanoma cell-intrinsic PD-1 and its inhibition antagonizes immune checkpoint blockade, Nature Communications (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-51496-2
Brigham and Women’s Hospital
Citation:
Exploring key regulators of programmed cell demise in melanoma and the immune system’s response (2024, August 28)
retrieved 28 August 2024
from
This doc is topic to copyright. Apart from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.