In an period the place expertise more and more merges with well being care to reinforce affected person outcomes, a examine performed by Fuyang Yu and his colleagues introduces an progressive strategy to decrease limb rehabilitation. Their analysis, revealed in Cyborg Bionic Systems, outlines the event of a decrease limb rehabilitation robotic designed to considerably enhance the security and effectiveness of gait coaching by means of a novel methodology based mostly on human-robot interplay pressure measurement.
Rehabilitation robots usually are not new, however the expertise behind them continues to evolve. Traditional fashions typically depend on predetermined gait patterns, which can not go well with each affected person’s wants, notably these with some residual muscle power. The crew’s new robotic addresses this by dynamically adjusting its gait in real-time to match the person’s intent and capabilities, a major shift from the extra frequent, passive coaching approaches.
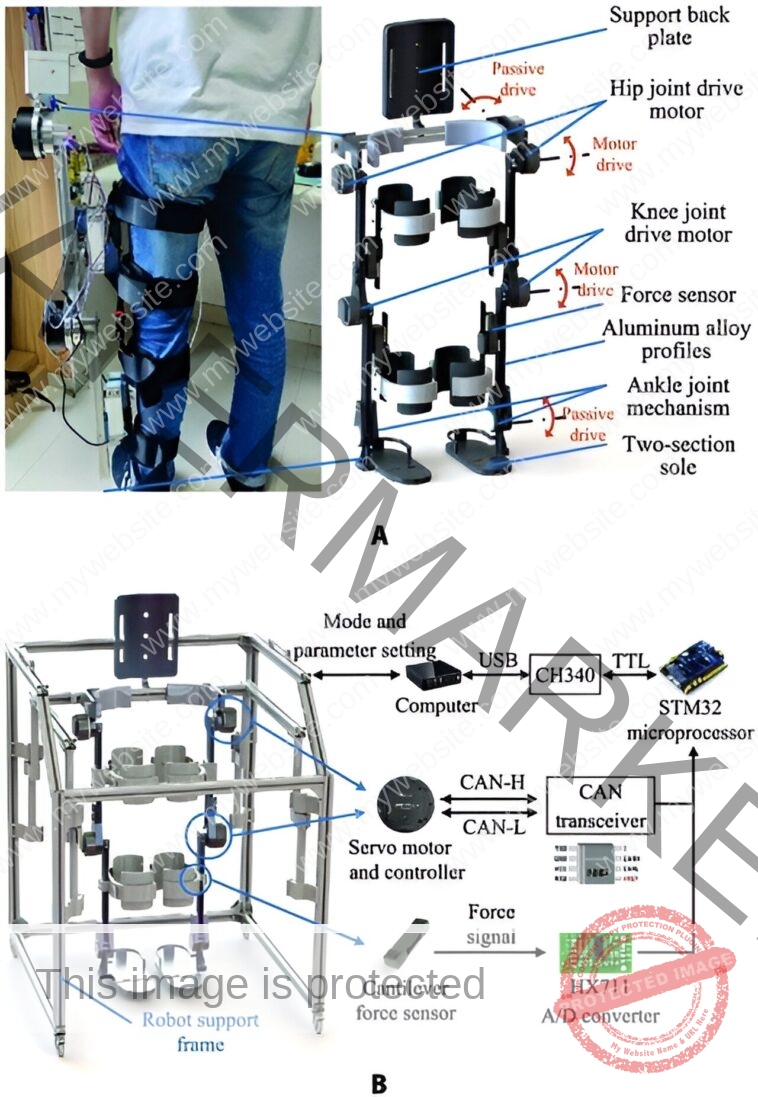
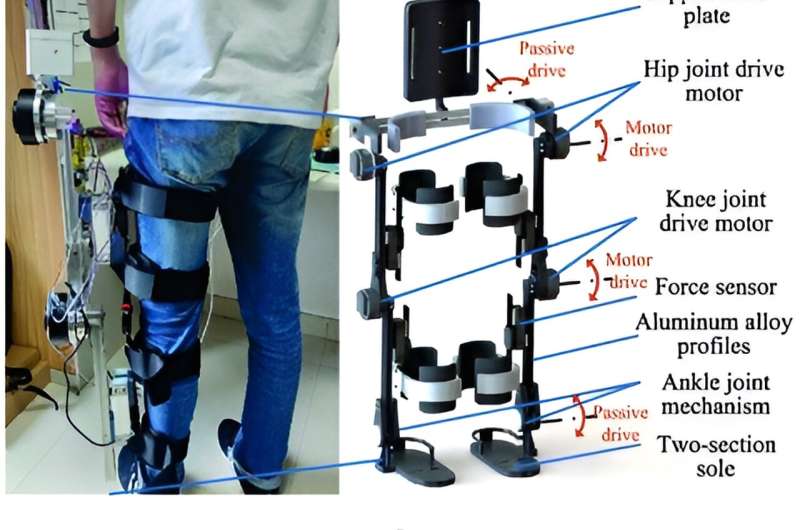
This robotic, developed by means of collaborative efforts by researchers at establishments together with the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences and the Institute of Automation on the Chinese Academy of Sciences, options an array of sensors and a complicated management system. These parts work collectively to measure the forces exerted by a affected person’s actions and regulate accordingly, guaranteeing that the robotic’s help is neither too little nor too extreme.
The core innovation lies in its adaptive gait coaching functionality. By utilizing face-to-face mounted cantilever beam pressure sensors, the robotic can precisely detect and interpret the refined forces exerted by the affected person throughout a coaching session. This information informs a dynamic mannequin that predicts and adapts the robotic’s actions in real-time, considerably enhancing the coaching’s responsiveness and effectiveness.
The analysis crew performed in depth testing to validate their design. Results from interactive experiments demonstrated that the robotic may considerably enhance the coaching expertise by responding to the affected person’s muscle inputs. This adaptability not solely maximizes engagement but in addition helps to forestall muscle atrophy and improves total restoration outcomes.
Moreover, this robotic represents a promising resolution for distant or underserved areas the place skilled medical and rehabilitation help could also be scarce. Its capability to supply customized coaching remotely may democratize entry to high-quality rehabilitation providers, making it a beneficial instrument in world well being contexts.
As well being care continues to embrace technological developments, the work of Yu and his crew showcases the potential of robotics in enhancing affected person care. Their growth not solely affords new hope for people with decrease limb impairments but in addition units a brand new commonplace for the mixing of clever expertise in therapeutic practices. This adaptive strategy may effectively develop into a cornerstone in the way forward for bodily rehabilitation, paving the way in which for extra responsive and efficient therapies.
More data:
Yu, F. et al. “Adaptive Gait Training of a Lower Limb Rehabilitation Robot Based on Human–Robot Interaction Force Measurement,” Cyborg and Bionic Systems (2024). DOI: 10.34133/cbsystems.0115, spj.science.org/doi/10.34133/cbsystems.0115
Provided by
Beijing Institute of Technology Press Co., Ltd
Citation:
Rehab robotics: A brand new leap in adaptive gait coaching (2024, August 21)
retrieved 22 August 2024
from
This doc is topic to copyright. Apart from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.