F. nucleatum, an oral anaerobe, is often related to colorectal most cancers and is linked to elevated most cancers cell proliferation, metastasis, and poor therapy outcomes.
Recent research have proven that F. nucleatum can set off autophagy in most cancers cells, resulting in elevated resistance to numerous chemotherapy medication. Additionally, F. nucleatum promotes an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment, hindering the infiltration of tumor-killing pure killer cells and T cells.
Therefore, eliminating F. nucleatum inside tumors may very well be a strategic strategy to reinforce therapeutic outcomes for colorectal most cancers. Antibiotics are broadly used to fight bacterial infections.
However, they usually indiscriminately kill each useful and dangerous micro organism, doubtlessly disrupting the intestinal microbiome. Bacterial vaccines supply a promising resolution by concentrating on particular pathogens with out harming the broader microbiome.
However, creating efficient bacterial vaccines is difficult because of the weak immunogenicity of main bacterial antigens. Although adjuvants can improve the humoral response, efficient vaccines require sturdy activation of antigen particular mobile response to get rid of intracellular pathogens.
Hence, there’s a robust need for an antibacterial vaccine able to eliciting sturdy immune responses to selectively eradicate F. nucleatum whereas preserving different microbiota.
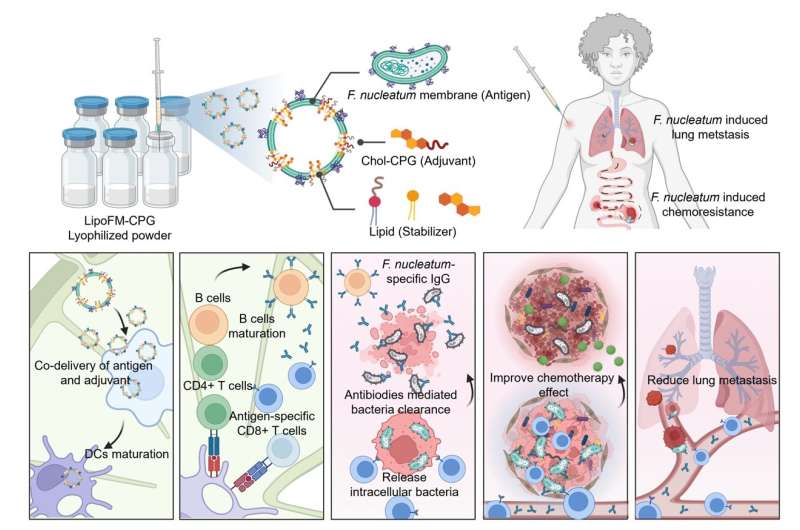
To handle these challenges, in an article revealed in Science Bulletin, a analysis staff led by Professor Qian Chen from Soochow University (Institute of Functional Nano & Soft Materials, FUNSOM) proposed a novel bacterial vaccine (LipoFM-CPG) by inserting cholesterol-modified agonist CpG into F.nucleatum derived membranes.
Compared with conventional emulsions with inactivated micro organism and Alum adjuvant, LipoFM-CPG co-delivers antigens and adjuvants, considerably enhancing dendritic cell maturation and antigen presentation.
This stimulation results in sturdy antibacterial mobile and humoral immune responses. The nanovaccine has demonstrated the power to selectively and effectively eradicate F. nucleatum, enhancing chemotherapy efficacy and decreasing most cancers metastasis in F. nucleatum-infected CRC.
Importantly, in comparison with systemic or oral antibiotics, the nanovaccine has a negligible affect on the intratumoral and intestine microbiota.
Overall, the work highlights a technique for designing a bacterial vaccine to elicit an immune response in opposition to intratumoral F. nucleatum, thereby potentiating most cancers therapy, and this nanovaccine with a easy manufacturing course of, robust immunogenicity, and desired biocompatibility, must be a promising expertise for selectively eliminating intratumoral micro organism and bettering the therapeutic impact in bacteria-infected most cancers.
More data:
Linfu Chen et al, An rising antibacterial nanovaccine for enhanced chemotherapy by selectively eliminating tumor-colonizing micro organism, Science Bulletin (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.scib.2024.06.016
Science China Press
Citation:
Innovations in most cancers therapy by way of focused bacterial vaccines (2024, August 29)
retrieved 29 August 2024
from
This doc is topic to copyright. Apart from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.