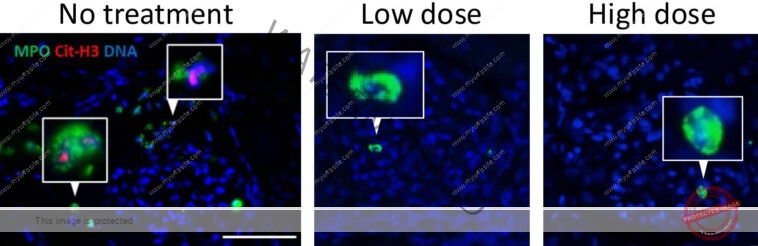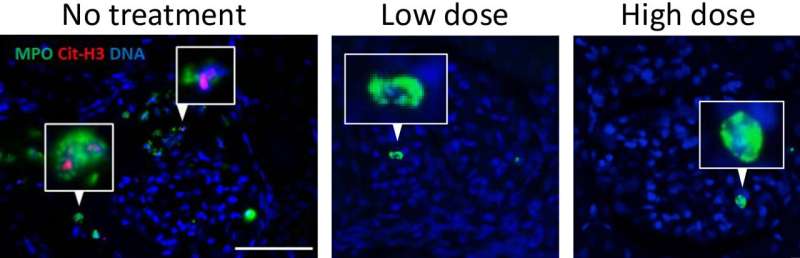
A newly developed compound that reduces dangerous irritation brought on by overactive neutrophils in rats exhibits nice potential as a safer therapy for numerous inflammatory illnesses in people.
Neutrophils are probably the most plentiful sort of white blood cells within the human physique, they usually play an important position in immune response. These immune cells assist struggle infections by engulfing pathogens and releasing enzymes that kill the invaders.
But though they’re important for combating infections, neutrophils can even grow to be overactive, main to varied inflammatory illnesses. When they’re activated by an infection, neutrophils can launch neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), web-like constructions consisting of DNA and proteins, which lure and kill pathogens as part of the conventional host protection mechanism. However, an excessive amount of NET formation can considerably injury tissues, thus contributing to irritation.
A crew of researchers from Hokkaido University and Alivexis, Inc., has investigated a recently-developed drug candidate, MOD06051, which reduces dangerous irritation in rat fashions by focusing on neutrophils. The outcomes of their joint analysis seem in Nature Communications.
“We discovered that MOD06051 works as a selective inhibitor for Cathepsin C (CatC), a key regulator that prompts a number of enzymes inside neutrophils generally known as neutrophil serine proteases (NSPs),” explains Yoh Terada, co-author from Alivexis, Inc. “One such NSP is neutrophil elastase, an enzyme concerned in killing pathogens but in addition a necessary issue for NET formation.”
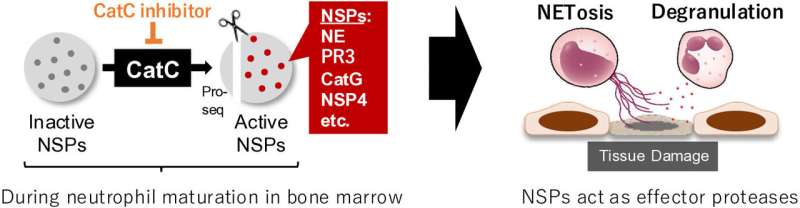
The scientists discovered that inhibiting CatC reduces the energetic type of neutrophil elastase and reduces the power of neutrophils to type NETs. Excessive NET formation has been linked to a number of illnesses, together with vasculitis, lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and diabetes.
“When we examined the compound in rats which have a selected sort of vasculitis, it decreased the illness severity, which was evident by lowered irritation and injury within the blood vessels, particularly of their kidneys and lungs,” says Professor Akihiro Ishizu, who led the examine.
“Our findings counsel that CatC inhibition exhibits promise as a brand new therapy technique to cut back neutrophil overactivation and enhance situations in illnesses the place overactive neutrophils and extreme NET formation play a crucial position. This strategy differs from present remedies which will have broader immunosuppressive results.”
Current remedies for inflammatory illnesses typically contain using glucocorticoids and immunosuppressive medication which suppress the immune system’s exercise as an entire and might result in secondary immunodeficiency, rising the chance of opportunistic infections. By particularly focusing on the activation of a number of NSPs by means of CatC inhibition with out broadly suppressing the immune system, MOD06051 probably affords a safer different that would cut back the chance of infections and different negative effects.
These findings pave the way in which for additional analysis and scientific trials to judge the security and efficacy of MOD06051 in people. The crew is optimistic that this novel strategy holds the promise of offering safer and more practical therapies for sufferers around the globe affected by a wide range of inflammatory illnesses, bettering their high quality of life.
More info:
Cathepsin C inhibition reduces neutrophil serine protease exercise and improves activated neutrophil-mediated issues, Nature Communications (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-50747-6
Hokkaido University
Citation:
New compound exhibits nice potential for sufferers with neutrophil-associated irritation (2024, August 22)
retrieved 22 August 2024
from
This doc is topic to copyright. Apart from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.